42 crossing the forked and pale mutants
Part a consider pea plants with the genotypes ggtt - Course Hero Part A - Determining relationships between alleles You decide to conduct a genetic analysis of these mutant lines by crossing each with a pure wild-type line. The numbers in the F 2indicate the number of progeny in each phenotypic class. Part A Consider pea plants with the genotypes GgTtand ggtt. Solved You continue your genetic analysis by crossing the | Chegg.com You continue your genetic analysis by crossing the forked and pale mutant lines with each other. The leaves of the F1 are light The F2 has six phenotypic classes, as shown below. the forked mutant allele as F (wild type = f+ ) and the pale mutant allele as p (wild type = P). Using these allele symbols, identify
(Get Answer) - You continue your nahin by crossing the Aberdeen White ... Part B - Crossing the forked and pale mutants You continue your genetic analysis by crossing the forked and pale mutant lines with each other. The leaves of the F1 are light green (intermediate between pale and wild-type leaves) and forked. The F2... Posted 11 months ago View Answer Q:
Crossing the forked and pale mutants
The Sex-Linked Group of Mutant Characters in Drosophila willistoni Since no forked females were obtained, it is possible that this was the original appearance of the mutant and that all of the forked flies were from one mother, heterozygous for forked. Forked-2 (f2) Description.-This character is much more extreme than its allelomorph, forked, or the similar mutant, stub- by. › parks › sum1471mC. T. Bauer College of Business at the University of Houston 1. (50 points)The textarea shown to the left is named ta in a form named f1.It contains the top 10,000 passwords in order of frequency of use -- each followed by a comma (except the last one). (Solved) You continue your genetic analysis by crossing the forked and ... You continue your genetic analysis by crossing the forked and pale mutant lines Replies Answer accepted by topic starter Solved Two lines of work indicated that crossing over actually involves breakage and re Solved An absorption line spectrum, with dark lines crossing the rainbow...
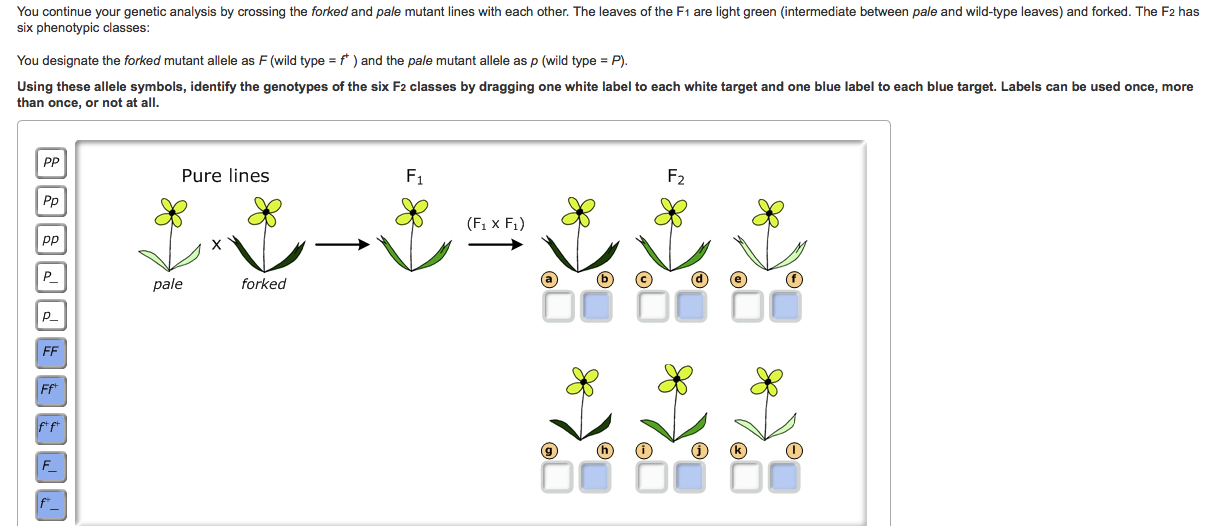
Crossing the forked and pale mutants. Part C - Crossing the forked and twist mutants You ... - Transtutors Expert's Answer. Part B - Crossing the forked and pale mutants You continue your genetic analysis by crossing the forked and pale mutant lines with each other. The leaves of the F1 are light green (intermediate between pale and wild-type leaves) and forked. The F2... Bio 181 Ch. 14 HW Flashcards | Quizlet Part B - Crossing the forked and pale mutants You continue your genetic analysis by crossing the forked and pale mutant lines with each other. The leaves of the F1 are light green (intermediate between pale and wild-type leaves) and forked. The F2 has six phenotypic classes, as shown below. Mastering bio ch.11 Flashcards | Quizlet Part B - Crossing the forked and pale mutants You continue your genetic analysis by crossing the forked and pale mutant lines with each other. The leaves of the F1 are light green (intermediate between pale and wild-type leaves) and forked. Solved You continue your genetic analysis by crossing the - Chegg You continue your genetic analysis by crossing the forked and pale mutant lines with each other. The leaves of the F1 are light green (intermediate between pale and wild-type leaves) and forked. The F2 has six phenotypic classes: You designate the forked mutant allele as F (wild type = f+ ) and the pale mutant allele as p (wild type = P).
› document › 491855170CoNLL17 Skipgram Terms | PDF | Foods | Beverages - Scribd CoNLL17 Skipgram Terms - Free ebook download as Text File (.txt), PDF File (.pdf) or read book online for free. Naruto Wallpaper Gifs Get The Best Gif On Giphy - Blogger Crossing The Forked And Pale Mutants : Frontiers Recombination Is Responsible For The Increased Recovery Of Drug Resistant Mutants With Hypermutated Genomes In Resting Yeast Diploids Expressing Apobec Deaminases Genetics You continue your genetic analysis by crossing the forked a… Part B - Crossing the forked and pale mutants You | Chegg.com Part B - Crossing the forked and pale mutants You continue your genetic analysis by crossing the forked and pale mutant lines with each other. The leaves of the F1 are light green (intermediate between pale and wild-type leaves) and forked. The F2 has six phenotypic classes, as shown below. Part b crossing the forked and pale mutants the green You designate the forkedmutant allele as F(wild type =f+) and the pale mutant allele as p(wild type =P). 1. Consider the alleles for leaf color first. Drag the white labels to the white targets to identify the genotype of each F 2class. Remember that p(the pale mutant allele) and P(the wild-type allele) are incompletely dominant to each other. 2.
Mastering Biology Chp. 14 HW Flashcards - Quizlet PART B - Crossing the forked and pale mutants You continue your genetic analysis by crossing the forked and pale mutant lines with each other. The leaves of the F1 are light green (intermediate between pale and wild-type leaves) and forked. The F2 has six phenotypic classes, as shown below. BIOL 2300 MasteringGen Ch. 4 - Subjecto.com Part B: Crossing the forked and pale mutants You continue your genetic analysis by crossing the forked and pale mutant lines with each other. The leaves of the F1 are light green (intermediate between pale and wild-type leaves) and forked. The F2 has six phenotypic classes: You designate the forked mutant allele as F (wild type = f+ ) and the ... Crossing The Forked And Pale Mutants - Blogger Crossing the forked and pale mutants. You continue your genetic analysis by crossing the forked and pale mutant . They, along side skinny pale mutants, are the only kind of mutants found in the caves. A black guinea pig crossed with an albino guinea pig produced twelve black. Pale mutants stand tall, and move in a very human like manner. Mastering Biology Chp. 14 HW - Subjecto.com You continue your genetic analysis by crossing the forked and pale mutant lines with each other. The leaves of the F1 are light green (intermediate between pale and wild-type leaves) and forked. The F2 has six phenotypic classes, as shown below. You designate the forked mutant allele as F (wild type = f+ ) and the pale mutant allele as p (wild ...
Week 8 Practice Problems_ Genetics I.pdf - 2019/11/3 Week... The mutant allele is dominant to its corresponding wildtype allele. Part B - Crossing the forked and pale mutants You continue your genetic analysis by crossing the forked and pale mutant lines with each other. The leaves of the F1 are light green (intermediate between pale and wild-type leaves) and forked.
CarlosghopStephens Crossing the forked and pale mutants You continue your genetic analysis by crossing the forked and pale mutant lines with each other. Determining Relationships between alleles. You decide to conduct a genetic analysis of these mutant lines by crossing each with a pure-breeding wild-type line. You de Post a Comment ...
Chapter 4 Flashcards | Quizlet A pure-breeding plant with red flowers is crossed to a pure-breeding plant with white flowers. All their progeny have flowers with some red patches and some white patches. Heterozygotes express both alleles. The color dilution gene in horses is an example of incomplete dominance. True
Sangat indah Crossing The Forked And Pale Mutants : Frontiers Recombination Is Responsible For The Increased Recovery Of Drug Resistant Mutants With Hypermutated Genomes In Resting Yeast Diploids Expressing Apobec Deaminases Genetics You continue your genetic analysis by crossing the forked a…
Incomplete Dominance and Codominance You are studying leaf development ... You identify several mutants of interest in this plant and make pure (true-breeding) lines of each mutant for further study. Part A - Determining relationships between alleles You decide to conduct a genetic analysis of these mutant lines by crossing each with a pure wild-type line. The numbers in the F2 indicate the number of progeny in each ...
Solved You continue your genetic analysis by crossing the - Chegg You continue your genetic analysis by crossing the forked and pale mutant lines with each other. The leaves of the F1 are light green (intermediate between pale and wild-type leaves) and forked. The F2 has six phenotypic classes: You designate the forked mutant allele as F (wild type = f+) and the pale mutant allele as p (wild type = P).
Part b crossing the forked and pale mutants you - Course Hero You designate the forked mutant allele as F(wild type = f+) and the pale mutant allele as p (wild type =P). 1. Consider the alleles for leaf color first. Drag the white labels to the white targets to identify the genotype of each F 2class. Remember that p(the pale mutant allele) and P (the wild-type allele) are incompletely dominant to each other.
BIOL 2300 MasteringGen Ch. 4 Flashcards - Quizlet You continue your genetic analysis by crossing the forked and pale mutant lines with each other. The leaves of the F1 are light green (intermediate between pale and wild-type leaves) and forked. The F2 has six phenotypic classes: You designate the forked mutant allele as F (wild type = f+ ) and the pale mutant allele as p (wild type = P).
CH 14 HW.docx - Course Hero You continue your genetic analysis by crossing the forked and pale mutant lines with each other. The leaves of the F 1 are light green (intermediate between pale and wild-type leaves) and forked. The F 2 has six phenotypic classes, as shown below. You designate the forked mutant allele as F (wild type = f +) and the pale mutant allele as p ...
Stanford University UNK the , . of and in " a to was is ) ( for as on by he with 's that at from his it an were are which this also be has or : had first one their its new after but who not they have
(Get Answer) - Part D - Assigning genotypes for codominant alleles You ... Assigning genotypes for codominant alleles You decide to designate the twist allele as FT to distinguish it from the forked allele F. Using the following allele symbols, identify the genotypes of the three F2 classes in Part C by dragging one label to each class. Labels may be used once, more than once, or not at all. Expert's Answer Solution.pdf
(Solved) You continue your genetic analysis by crossing the forked and ... You continue your genetic analysis by crossing the forked and pale mutant lines Replies Answer accepted by topic starter Solved Two lines of work indicated that crossing over actually involves breakage and re Solved An absorption line spectrum, with dark lines crossing the rainbow...
› parks › sum1471mC. T. Bauer College of Business at the University of Houston 1. (50 points)The textarea shown to the left is named ta in a form named f1.It contains the top 10,000 passwords in order of frequency of use -- each followed by a comma (except the last one).
The Sex-Linked Group of Mutant Characters in Drosophila willistoni Since no forked females were obtained, it is possible that this was the original appearance of the mutant and that all of the forked flies were from one mother, heterozygous for forked. Forked-2 (f2) Description.-This character is much more extreme than its allelomorph, forked, or the similar mutant, stub- by.

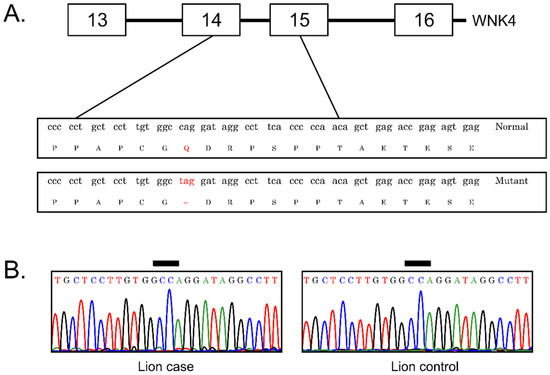


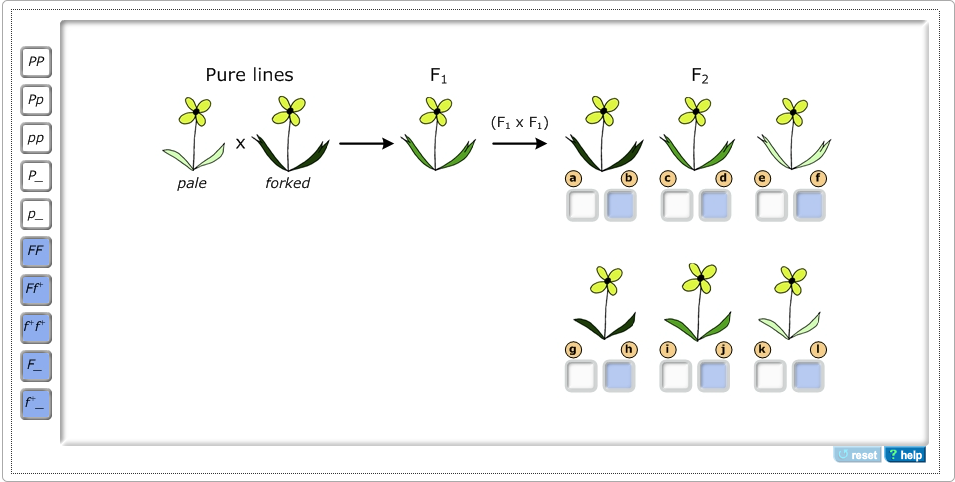




















Post a Comment for "42 crossing the forked and pale mutants"